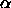 , of
the cirrus emission power; 2.) the power at 0.01 arcmin
, of
the cirrus emission power; 2.) the power at 0.01 arcmin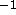 ,
,
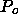 (0.01/arcmin); and 3.) the observing geometry.
(0.01/arcmin); and 3.) the observing geometry.
We base our discussion of confusion by infrared cirrus on the
formalism of Gautier et al. (1992). To apply these results, we
need to set three parameters: 1.) the power law index, 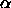 , of
the cirrus emission power; 2.) the power at 0.01 arcmin
, of
the cirrus emission power; 2.) the power at 0.01 arcmin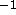 ,
,
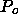 (0.01/arcmin); and 3.) the observing geometry.
(0.01/arcmin); and 3.) the observing geometry.
Analysis of the IRAS far infrared data shows that the cirrus
power spectrum has a spectral index of 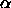 = -2.6 to -3.2
(Gautier et al. 1992, T. N. Gautier unpublished work). The IRAS
data do not extend to the high spatial frequencies that are
important for future missions that will have both telescopes of
larger aperture and imaging far infrared arrays. However, the
power spectrum can be estimated at these high frequencies by
comparison with deep CCD exposures in the visible, which can reach
1 arcsec
= -2.6 to -3.2
(Gautier et al. 1992, T. N. Gautier unpublished work). The IRAS
data do not extend to the high spatial frequencies that are
important for future missions that will have both telescopes of
larger aperture and imaging far infrared arrays. However, the
power spectrum can be estimated at these high frequencies by
comparison with deep CCD exposures in the visible, which can reach
1 arcsec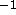 . Cutri (private communication) finds that the
power spectrum steepens slightly from the low spatial frequencies
(i.e., à becomes more negative). In the following, we will assume
. Cutri (private communication) finds that the
power spectrum steepens slightly from the low spatial frequencies
(i.e., à becomes more negative). In the following, we will assume
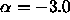 .
.
The level of cirrus contamination is characterized by 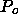 .
As a medium level of cirrus contamination, we adopt the average
.
As a medium level of cirrus contamination, we adopt the average
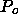 for
for 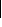 b
b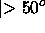 , namely
, namely 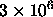 Jy
Jy /sr
(Gautier et al. 1992). Other levels of cirrus emission are listed
in Table II.
/sr
(Gautier et al. 1992). Other levels of cirrus emission are listed
in Table II.
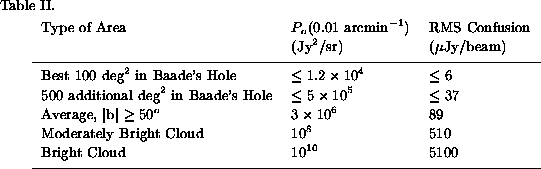
Table ii: Cirrus Confusion Noise at 100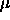 m
m
Because of the steep power spectrum of the cirrus emission,
there is a premium in keeping the reference field as tightly
coupled to the source as possible. We have therefore computed the
cirrus confusion noise assuming an annular reference field that
lies between 0.6 and 1.6 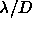 . For comparison with the
galaxy confusion limit, we have interpolated to an effective beam
diameter of 0.8
. For comparison with the
galaxy confusion limit, we have interpolated to an effective beam
diameter of 0.8 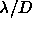 . Because of the low power at high
spatial frequencies, the noise from cirrus confusion is only weakly
dependent on the beam diameter but very strongly on the reference
area size.
. Because of the low power at high
spatial frequencies, the noise from cirrus confusion is only weakly
dependent on the beam diameter but very strongly on the reference
area size.
For the case of an 85 cm telescope, the resulting cirrus
confusion noise limit at the average level of high latitude cirrus
emission is 89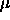 Jy per beam, with these assumptions. Values for
the rms confusion noise for the 85 cm telescope at other
wavelengths and in other parts of the sky are entered in Table II.
The confusion noise will scale as the square root of
Jy per beam, with these assumptions. Values for
the rms confusion noise for the 85 cm telescope at other
wavelengths and in other parts of the sky are entered in Table II.
The confusion noise will scale as the square root of 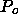 and as
and as
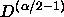 , i.e., as
, i.e., as 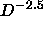 for
for 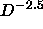 .
.